What is a Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of proxy servers in geographically distributed data centers that improve service availability and performance for users accessing your website, content, or applications from around the world.
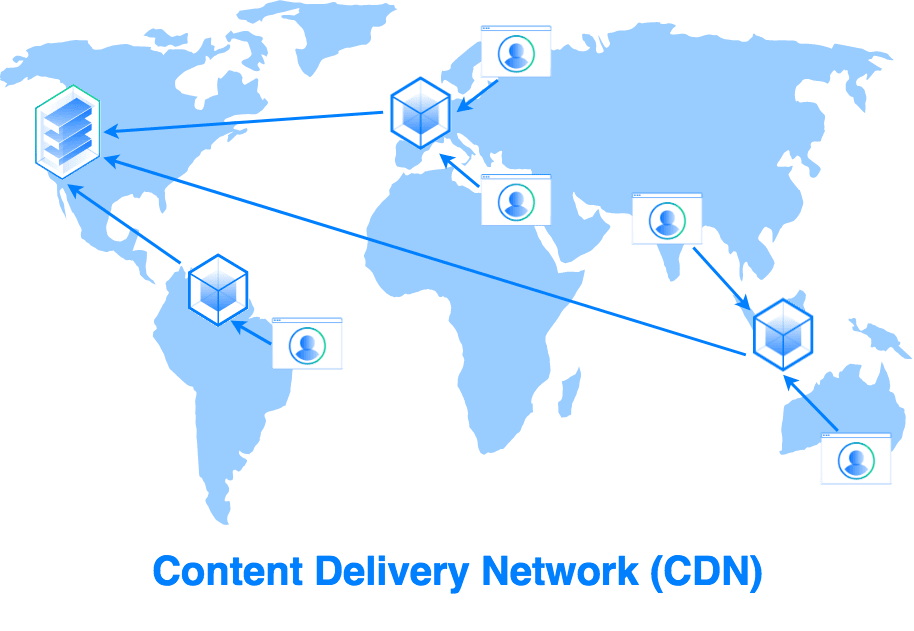
How Does a CDN Work?
Content delivery networks (CDNs) are designed to reduce network latency when serving content over the Internet to users distributed around the world.
The world’s largest CDN provider, Akamai, maintains a global network of more than 325,000 servers, residing in more than 1,400 networks across 135 countries. The Akamai CDN is within a single network hop for 85% of Internet users, and is estimated to route between 15 and 30% of all traffic on the Internet.
Organizations that serve content over the Internet, including SaaS companies, web publishers, and video streaming services can contract with Akamai to store data on Akamai servers and deliver it to their customers via the Akamai CDN. Akamai’s extensive global network brings these assets and services physically closer to the end user, resulting in faster access and minimizing latency.
Founded in 1998, Akamai was a very early entrant in the CDN marketplace. The marketplace for CDN providers in 2023 includes free CDNs, traditional commercial CDN providers, public cloud CDN services, and proprietary CDNs operated by telecommunications companies. Well-known alternatives to Akamai include StackPath, Cloudflare, Fastly, Imperva, and Amazon CloudFront.
Why is a CDN Important?
The end result of implementing a CDN for your website, SaaS application, or streaming service is improved speed, performance, and availability for the end users who access your content over the Internet.
For websites that serve content to users around the world, CDNs deliver enhanced website performance in the form of faster page loading speeds. This matters for two important reasons:
- Customer Satisfaction – Slow page loading times have been shown to reduce customer satisfaction and impact the commercial success of your website, application, or service. Even a one-second delay in page loading time corresponds to a measurable drop in conversions and on-page engagement.
Implementing a CDN helps minimize your page loading times as much as possible, so you can deliver the best possible experience for customers accessing your digital content or apps from around the world. - SEO Performance – Pages that take longer to load have an elevated bounce rate compared to those that load more quickly. A bounce rate measures how frequently users exit a page on your website without interacting.
When users access your website or application via the Google chrome browser, Google measures the aggregate bounce rate. High bounce rates are used as an indicator of poor customer experiences and can make your website less likely to appear in the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
Implementing a CDN accelerates access to your content for users around the world, reducing the risk of an elevated bounce rate that could impact your SEO performance.
Four Benefits of a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
1. Reducing Latency
CDNs were originally developed to help reduce latency on the Internet, defined as the delay between when you request content from a server and when the content actually loads on your screen.
One of the main causes of latency is the physical distance between the user and the server where the content is being hosted. Content on a server in San Francisco might be accessed by a user in Sacramento with minimal latency, but another user in Eastern Africa might experience significant latency due to their physical distance from the server.
A CDN allows content from the origin server to be mirrored and cached on proxy servers
2. Website Reliability and Redundancy
A CDN makes your website or application available on hundreds or even thousands of servers around the world. If some of those servers become unavailable, there are still plenty more servers that can deliver your content to users. This makes your website or SaaS application more resilient against unplanned outages.
3. Reducing Bandwidth Costs
Bandwidth costs are one of the main expenses associated with hosting a website or delivering a SaaS application. CDN providers use caching and other types of storage optimization to reduce bandwidth costs for their customers.
4. Digital Security
If your website or SaaS application is the target of a Denial of Service (DoS) attack, your CDN can route malicious traffic away from your origin server to ensure that your services remain available for customers.
Maximize Marketing Success with a CDN
As the leading SaaS SEO agency, Directive’s customer generation methodology depends on CDNs and other technologies that allow us to optimize customer experiences, accelerate on-page conversions, and fully capitalize on the Total Addressable Market (TAM) for our B2B SaaS clients.
Ready to learn more?
Book an intro call with Directive, or Join Society for exclusive access to content, insights, and advice from our SaaS marketing community.