What is User Experience?
Businesses place much of their focus on designing and building products that meet the needs of the intended user. While it is clear that products and services should solve the customer’s problems, there are many factors beyond the effectiveness of the product that contribute to overall customer satisfaction. Today, businesses are increasingly recognizing the need to go further than product design and deliver an exceptional user experience that promotes customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
User experiences encompass every aspect of a user’s interactions with your brand, services, and products across all channels. The user experience begins when a prospective customer first interacts with your brand and extends beyond the initial purchase to include the experiences the customer has while using the product. User experience design can be applied to the product marketing and sales process and to digital products themselves to promote ease of use and drive customers towards desired outcomes.
User experience (UX) ultimately comes down to meeting the needs of the customer, which are highly context-dependent. To refine their UX design, businesses should focus on understanding the needs of the customer in every interaction with the company, its services, and its product, capturing those needs as design inputs and finding solutions that help the customer get what they want as easily as possible.
Why is User Experience Important?
Don Norman, an American cognitive scientist who first coined the term “User Experience” imagined a product as a cohesive, integrated set of experiences for the customer. These experiences began at the first interaction with the company and extended throughout the entire product life cycle.
User experience design is the most important aspect of building and marketing a website that meets the needs of your customers and drives them toward target behaviors. Website UX design enhances user satisfaction by making websites easier to use, efficient to navigate and accessible for users on a variety of devices. UX designers implement changes and updates that enhance the user experience, helping more of your customers find what they’re looking for and resulting in more leads, conversions, and opportunities for your sales team.
Components of a Meaningful and Valuable User Experience
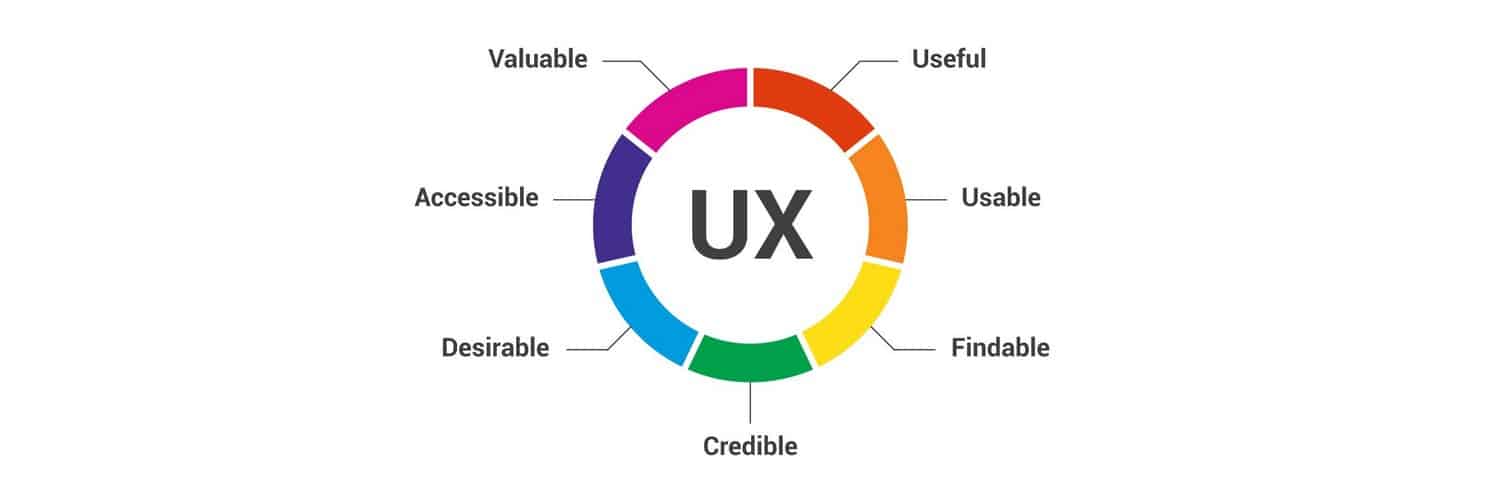
Delivering an exceptional user experience requires a deep understanding of what your users want, what their values are, what they’re looking for and what tools they need to accomplish their goals. The objective of UX design is to use this information to drive customer satisfaction in every interaction while funneling prospects towards a desired activity or outcome. Consider the following components of meaningful and valuable user experience design for a website:
- Accessibility – Content should be accessible for persons with disabilities. Developers should ensure that the website presents well on a variety of devices, including mobiles, laptops and even on television screens. Responsive design is a must as mobile shopping and browsing continue to grow.
- Credibility – Content should be credible and your company should strive to earn the trust and confidence of prospects in each interaction.
- Desirability – Website design elements should reflect a brand image and identity that customers would like to be associated with.
- Findability – Content should be easy to find and navigate. The customer should be able to get the answers they need or navigate to the page they’re looking for with minimal effort. Intuitive navigation and organization are important features.
- Usability – The website should be easy to use.
- Usefulness – Content, products, and services should be useful to the customer, addressing the customer’s needs and meeting them as comprehensively as possible.
An effective user experience designer incorporates elements of visual design, content strategy and design, user interface and website design and more. User research may be conducted to help the designer further understand the unique contextual needs of the customer and how to design an experience that best meets those requirements.
How to Measure User Experience
If you want to start improving your user experience, you need to be able to measure success and failure. Thanks to digital analytical tools, businesses can capture a range of valuable metrics that reflect how customers interact with their advertisements, web pages, content, shopping carts, and other touchpoints. There are two types of metrics commonly used to evaluate and improve user experience.
Behavioral User Experience Metrics
Measuring user behavior as they interact with your brands, products, and services across touchpoints is an effective way of improving your user experience over time. Website analytics can be used to understand how customers interact with each page and how individual pages or the website as a whole can be designed to help customers accomplish their intended goals faster and with less effort.
Commonly tracked behavioral UX metrics include:
- Shopping Cart Abandonment Rate – How frequently did a customer put items into their shopping cart but leave the website without purchasing? Customers may abandon carts because of high shipping costs or a lack of payment options.
- Bounce Rate – A measure of the total percentage of users that land on your website and leave quickly without visiting any other pages.
- Page Views/Visit Time – How long does the average user spend on the website? How many pages do they view?
- Task Success – A task success is another way of describing a “conversion”. If you can measure how frequently a user successfully completes a task (reaches a specified stage in check-out flow, completes an e-mail submission form, etc.), you can start discovering ways to increase that conversion rate.
- Task Time – How long does it take for users to complete their desired task in customer interaction? If the goal is to engage the user, longer task times might be better. If the goal is to provide convenience and help the user save time, shorter task times are preferred.
Attitudinal User Experience Metrics
Attitudinal UX metrics measure user experience by asking the customer how they felt about their experience. Instead of measuring user behavior directly, attitudinal metrics are assessed by having the customer report how they felt about their experience and encouraging them to provide feedback.
Commonly tracked attitudinal UX metrics include:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) – A score calculated from survey responses that measure how likely a customer would be to recommend your product or service to their family and friends.
- System Usability Scale (SUS) – A website usability test offers a proposition like “This website made it easy to find what I was looking for” and invites respondents to rate their level of agreement with the proposition. This simple survey makes it easy to collect feedback on whether you’re delivering a great user experience, but you’ll have to do additional work to understand if/why users are running into difficulties and how you can make their lives easier.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) – Customer satisfaction surveys are used everywhere from eCommerce stores to restaurants. Usually presented in a survey format, they offer a simple way for businesses to collect feedback on the user experience and identify opportunities for improvement.
Directive Consulting Offers User Experience Design for Enterprise Brands
At Directive Consulting, we’re experts in conversion rate optimization (CRO). Our seasoned user experience designers leverage individual expertise and deep organizational knowledge garnered through years of successful UX design projects to help optimize your website for your customers, boost your conversion rate and volume and drive down customer acquisition costs.
Ready to learn more? Contact us for a free proposal.